Table of contents
Open Table of contents
介绍
什么是 Store
Store是一个保存状态和业务逻辑的实体,它并不与你的组件树绑定。换句话说,它承载着全局状态。它有点像一个永远存在的组件,每个组件都可以读取和写入它。
Vuex
Vuex就是一个专为 Vue 应用程序开发的Store。它用于管理 Vue 应用中的共享状态,使得多个组件能够方便地访问和修改相同的数据。Vuex的核心概念包含state、mutations、actions和getters等。
Pinia
Pinia是一个专为 Vue 3 设计的Store。它是在 Vue 3 响应式 API 的基础上构建的,旨在提供一种轻量、灵活且直观的状态管理解决方案。与传统的Vuex不同,Pinia不依赖于全局对象,而是通过创建独立的store实例来管理状态。state、getter和action是Pinia的三个重要概念。
安装
- vuex
yarn add vuex@next --save
# 或者使用 npm
npm install vuex@next --save- pinia
yarn add pinia
# 或者使用 npm
npm install pinia注意:实际项目开发可不要即用Vuex又用Pinia,除非公司是你家开的。
创建与使用
vuex
- 在自己项目的
src目录下创建一个store目录,再创建一个index.js,在这里我们创建 Vuex 的store实例。
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
const store = createStore({
//需要管理的数据存放在这里
state() {
return {
msg: "hello vuex",
};
},
//唯一可以同步修改state的地方
mutations: {
},
//异步修改state,本质还是通过mutations修改
actions: {
},
//类似于vue中的计算属性computed
getters: {
},
//如果需要vuex管理的数据多的话,可以拆分为一个个模块
modules: {
}
})
export default store;
- 在
main.js中引入刚刚创建的实例store
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from './store'
createApp(App).use(store).mount('#app')- 在App.vue中使用:
<template>
<div>
{{store.state.msg}}
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
let store = useStore()
</script>
如果页面成功显示hello vuex,恭喜你,已经成功创建了一个Vuex Store实例。
Pinia
- 同理,在
src目录下创建一个store目录,在index.js中创建 Pinia 的store实例:
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const store = defineStore('store',{
state: ()=>{
return {
msg:'hello pinia',
}
},
getters: {},
actions: {}
})
- 在
main.js中引入创建的 Pinia 实例:
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
const pinia = createPinia()
createApp(App).use(pinia).mount('#app')
- 在
App.vue中使用:
<template>
<div>
{{storeA.msg}}
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { store } from './store';
let storeA = store()
</script>
如果页面成功显示hello pinia,恭喜你 Pinia 实例创建成功~
修改状态
Vuex
- 在组件中直接修改
<template>
<div>
{{store.state.msg}}
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
let store = useStore()
store.state.msg = 'hello juejin' //直接赋值修改
</script>
方法可行,但是这样直接修改状态会绕过 Vuex 的mutation操作,破坏了单向数据流的概念。Vuex 还是推荐通过mutations来修改状态,以确保状态的变化是可追踪的。
- 在mutations中修改
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
const store = createStore({
//需要管理的数据存放在这里
state() {
return {
msg: "hello vuex",
};
},
//唯一可以同步修改state的地方
mutations: {
changeMsg(state,data){
state.msg = data
}
},
......
})
export default store;
- 在组件中用commit触发状态变更:
<template>
<div>
{{store.state.msg}}
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
let store = useStore()
store.commit('changeMsg','hello juejin')//commit触发状态变更
</script>
- 在actions中进行提交mutations进行修改
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
const store = createStore({
state() {
return {
msg: "hello vuex",
};
},
mutations: {
changeMsg(state, data) {
state.msg = data
}
},
//异步通过mutations修改state
actions: {
async getMsg({ commit }, newMsg) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('changeMsg', newMsg);
}, 1000);
}
},
......
})
export default store;
- 在组件中使用dispatch进行分发actions
<template>
<div>
{{store.state.msg}}
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
let store = useStore()
store.dispatch('getMsg','hello juejin') //dispatch分发
</script>
这里我们在actions中设置了一个一秒的定时器,来模拟异步操作,使用一进入页面,显示的还是hello vuex,但一秒后就变成hello juejin了。
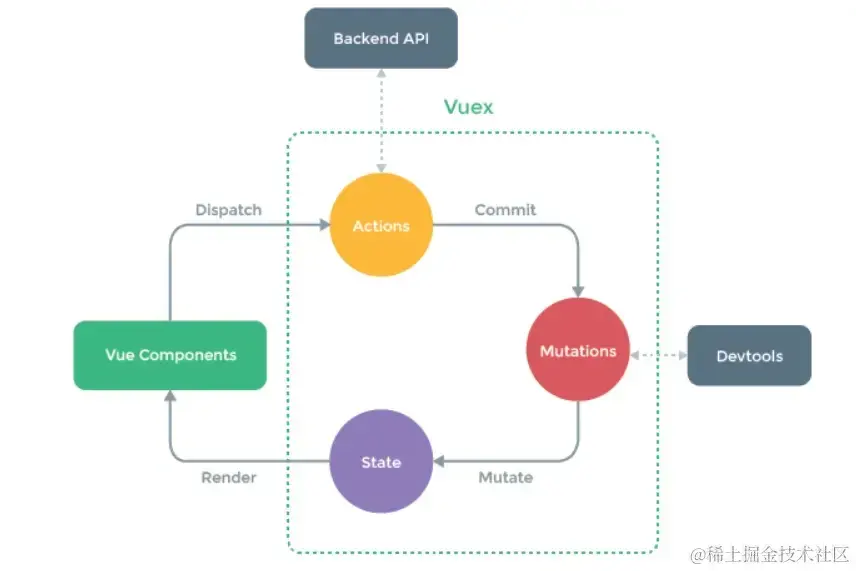
vuex的数据流程
简单概述
就是组件通过调用dispatch触发一个Action,Action的处理函数执行一些异步操作,然后提交一个Mutation,Mutation的处理函数修改State,State的变化触发视图的更新。
Pinia
- 在组件中直接修改
<template>
<div>
{{storeA.msg}}
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { store } from './store';
let storeA = store()
storeA.msg = 'hello juejin'
console.log(storeA.msg);
</script>
- 使用$patch方法
使用$patch方法可以修改一个或多个状态
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const store = defineStore('store',{
state: ()=>{
return {
msg:'hello pinia',
name:'yangyangyang'
}
},
getters: {},
actions: {}
})
- 在组件中进行修改
<template>
<div>
{{storeA.msg}}
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { store } from './store';
let storeA = store()
console.log(storeA.msg,storeA.name);
storeA.$patch({
msg:'hello juejin',
name:'miemiemie'
})
console.log(storeA.msg,storeA.name);
</script>
-
在actions中进行修改
-
与 Vuex 的
actions不同,Pinia中的actions既可以是同步也可以是异步,由于 Pinia 中没有mutations,所以工作都交给了actions。
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const store = defineStore('store',{
state: ()=>{
return {
msg:'hello pinia',
name:'yangyangyang'
}
},
actions: {
changeMsg(data){
this.msg = data
}
},
getters: {},
})
- 直接在组件中调用
changeMsg方法,而不用像 Vuex 一样dispatch进行分发。
<template>
<div>
{{storeA.msg}}
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { store } from './store';
let storeA = store()
storeA.changeMsg('hello juejin')
</script>
重置 state
- 使用选项式 API时,可以通过调用 store 的
$reset()方法将 state 重置为初始值。
<script setup>
import { store } from './store';
let storeA = store()
storeA.changeMsg('hello juejin')
console.log(storeA.msg);
storeA.$reset()
console.log(storeA.msg);
</script>
模块化
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。为了解决以上问题,对 Vuex 或 Pinia 进行模块化开发至关重要,尤其是对于大型项目。
Vuex
Vuex 允许我们将 Store 拆分成多个模块(module),每个模块都有自己的
State、Mutation、Action和Getter。
一般项目开发中,我们都会将每个module单独存放在一个文件中,然后再引入总入口store/index.js中
-
在
src目录下创建一个modules文件夹,然后在其中创建你的模块文件。 -
模块A
//modules/moduleA.js
const moduleA = {
state: () => ({
msg:'hello moduleA'
}),
mutations: {},
actions: {},
getters: {}
}
export default moduleA
- 模块B
//modules/moduleB.js
const moduleB = {
state: () => ({
msg:'hello moduleB'
}),
mutations: {},
actions: {},
getters: {}
}
export default moduleB
- 将各模块引入主模块
//store/index.js
import { createStore } from 'vuex';
import moduleA from '../modules/moduleA';
import moduleB from '../modules/moduleB';
const store = createStore({
modules: {
moduleA,
moduleB
}
})
export default store;
- 在组件中使用moduleA和moduleB
<template>
<div>
{{store.state.moduleA.msg}}
<br>
{{store.state.moduleB.msg}}
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
let store = useStore()
</script>
为了防止各模块中mutations或者actions中的方法重名引发的问题,modules提供了命名空间 的方法(namespaced: true)
- 以moduleA为例:
//modules/moduleA.js
const moduleA = {
namespaced: true,
state: () => ({
msg:'hello moduleA'
}),
mutations: {
changeMsg(state,data){
state.msg = data
}
},
actions: {},
getters: {}
}
export default moduleA
- 为了避免其他模块中也有相同命名的
changeMsg方法,我们可以通过 “模块名/方法名” 的方式调用。
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
let store = useStore()
console.log(store.state.moduleA.msg);
store.commit('moduleA/changeMsg','hello juejin')
console.log(store.state.moduleA.msg);
Pinia
Pinia 每个状态库本身就是一个模块。Pinia 没有modules,如果想使用多个Store,直接定义多个 Store传入不同的 ID (defineStore()的第一个参数)即可。
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const useModuleA = defineStore('storeA',{
state: () => (),
actions: {},
getters: {}
});
export const useModuleB = defineStore('storeB',{
state: () => (),
actions: {},
getters: {}
});
- 在组件中,要使用哪个模块就引入哪个模块。
import { useModuleA } from './store';
let storeA = useModuleA()
console.log(storeA.msg);
storeA.changeMsg('hello juejin')
console.log(storeA.msg);
最后
如果你的项目是基于 Vue 2,可以选择 Vuex,如果你的项目基于 Vue 3,喜欢使用组合式 API,使用 TS ,那么更推荐使用 Pinia。当然,具体根据个人和团队的具体情况来选择。感谢阅读✌🏻